中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (10): 1527-1531.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.10.009
• 药物控释材料 drug delivery materials • 上一篇 下一篇
异种骨/重组人骨形态发生蛋白7/纤维蛋白胶复合材料的缓释性能及成骨活性
张建华
- 河北沧州中西医结合医院,河北省沧州市 061000
Sustained release ability and osteogenic activity of xenogeneic bone/recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 7/fibrin glue composite material
Zhang Jian-hua
- Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
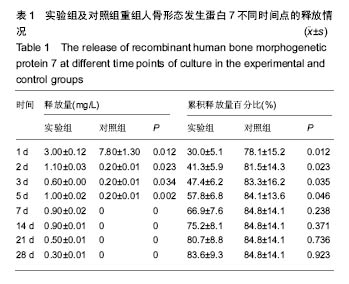
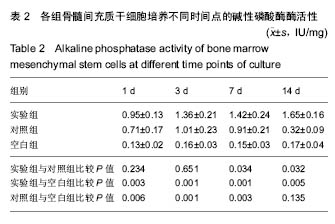
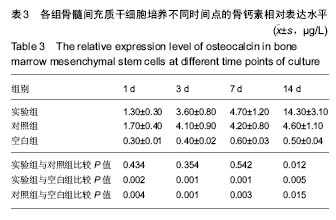
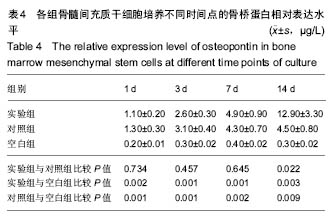
背景:骨形态发生蛋白的稳定缓慢释放是其诱导成骨作用的前提,因此需要合适的载体使骨形态发生蛋白缓慢释放,然而迄今为止还没有一种医学界公认的骨形态发生蛋白理想载体。 目的:评价异种骨复合材料中骨形态发生蛋白7的缓释情况及成骨活性。 方法:以异种小牛松质骨为支架材料,采用真空负压吸附法将含重组人骨形态发生蛋白7的溶液吸附在支架材料上,再喷涂纤维蛋白胶涂层,制备异种骨/重组人骨形态发生蛋白7/纤维蛋白胶复合材料,作为实验组材料;将小牛松质骨、小牛松质骨/重组人骨形态发生蛋白7复合材料分别作为空白组、对照组材料。将3组材料分别在PBS中持续浸泡28 d,观察重组人骨形态发生蛋白7的缓释情况;将3种材料分别与第3代髓间充质干细胞共培养,检测培养1,3,7,14 d的细胞碱性磷酸酶活性、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素表达水平。 结果与结论:①空白组无重组人骨形态发生蛋白7释放,实验组重组人骨形态发生蛋白7的缓释效果优于对照组;②实验组、对照组培养不同时间点的碱性磷酸酶活性、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素表达水平均高于空白组(P < 0.05),实验组培养14 d的细胞碱性磷酸酶活性、骨桥蛋白和骨钙素表达水平均高于对照组(P < 0.05);③结果表明:异种骨/重组人骨形态发生蛋白7/纤维蛋白胶复合材料具有良好的缓释性能及成骨活性。
ORCID: 0000-0003-2353-5481(张建华)
中图分类号:
.jpg)